Arduino Stepper Motor Serial Control Cable
- Arduino Stepper Motor Serial Control Cable Box
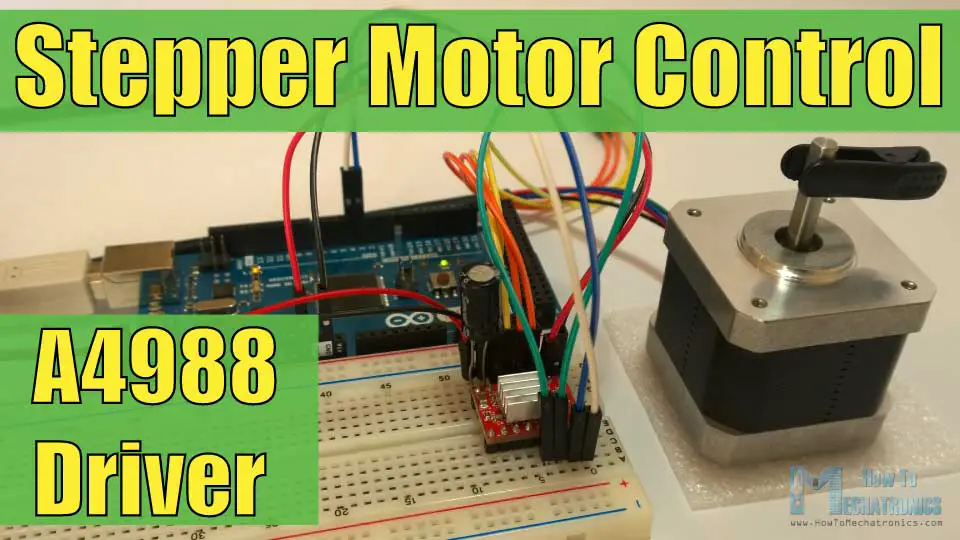
- Stepper Motor Arduino Circuit
- Stepper Motors And Arduino
The example code will control both kinds of motors. See the unipolar and bipolar motor schematics for information on how to wire up your motor. In this example, a potentiometer (or other sensor) on analog input 0 is used to control the rotational speed of a stepper motor using the Arduino Stepper Library. The stepper is controlled by with.
Stepper motors are increasingly taking its position in the world of the electronics. Starting from a normal Surveillance camera to a complicated CNC machines/Robot these Stepper Motors are used everywhere as actuators since they provide accurate controlling. In this tutorial we will learn about the most commonly/cheaply available stepper motor 28-BYJ48 and how to interface it with Arduino using ULN2003 stepper module.
In last project we have simply Interfaced Stepper Motor with Arduino, where you can rotate the stepper motor by entering the rotation angle in Serial Monitor of Arduino. Here in this project, we will Rotate the Stepper Motor using Potentiometer and Arduino, like if you turn the potentiometer clockwise then stepper will rotate clockwise and if you turn potentiometer anticlockwise then it will rotate anticlockwise.
Stepper Motors:
Let us take a look at this 28-BYJ48 Stepper motor.
Okay, so unlike a normal DC motor this one has five wires of all fancy colors coming out of it and why is it so? To understand this we should first know how a stepper works and what its specialty is. First of all steppers motors do not rotate, they step and so they also known as step motors. Meaning, they will move only one step at a time. These motors have a sequence of coils present in them and these coils have to be energized in a particular fashion to make the motor rotate. When each coil is being energized the motor takes a step and a sequence of energization will make the motor take continuous steps, thus making it to rotate. Let us take a look at the coils present inside the motor to know exactly know from where these wires come from.
As you can see the motor has Unipolar 5-lead coil arrangement. There are four coils which have to be energized in a particular sequence. The Red wires will be supplied with +5V and the remaining four wires will be pulled to ground for triggering the respective coil. We use a microcontroller like Arduino energize these coils in a particular sequence and make the motor perform the required number of steps.
So now, why is this motor called the 28-BYJ48? Seriously!!! I don’t know. There is no technical reason for this motor for being named so; maybe we should dive much deeper into it. Let us look at some of the important technical data obtained from the datasheet of this motor in the picture below.
That is a head full of information, but we need to look at few important ones to know what type of stepper we are using so that we can program it efficiently. First we know that it is a 5V Stepper motor since we energize the Red wire with 5V. Then, we also know that it is a four phase stepper motor since it had four coils in it. Now, the gear ratio is given to be 1:64. This means the shaft that you see outside will make one complete rotation only if the motor inside rotates for 64 times. This is because of the gears that are connected between the motor and output shaft, these gears help in increasing the torque.
Another important data to notice is the Stride Angle: 5.625°/64. This means that the motor when operates in 8-step sequence will move 5.625 degree for each step and it will take 64 steps (5.625*64=360) to complete one full rotation.
Calculating the Steps per Revolution for Stepper Motor:
It is important to know how to calculate the steps per Revolution for your stepper motor because only then you can program it effectively.
In Arduino we will be operating the motor in 4-step sequence so the stride angle will be 11.25° since it is 5.625°(given in datasheet) for 8 step sequence it will be 11.25° (5.625*2=11.25).
Steps per revolution = 360/step angle
Here, 360/11.25 = 32 steps per revolution.
Why so we need Driver modules for Stepper motors?
Most stepper motors will operate only with the help of a driver module. This is because the controller module (In our case Arduino) will not be able to provide enough current from its I/O pins for the motor to operate. So we will use an external module like ULN2003 module as stepper motor driver. There are a many types of driver module and the rating of one will change based on the type of motor used. The primary principle for all driver modules will be to source/sink enough current for the motor to operate.
Circuit Diagram for Rotating Stepper Motor using Potentiometer:
The circuit Diagram for the Controlling Stepper Motor using Potentiometer and Arduino is shown above. We have used the 28BYJ-48 Stepper motor and the ULN2003 Driver module. To energise the four coils of the stepper motor we are using the digital pins 8,9,10 and 11. The driver module is powered by the 5V pin of the Arduino Board. A potentiometer is connected to A0 based in whose values we will rotate the Stepper motor.
But, power the driver with External Power supply when you are connecting some load to the steppe motor. Since I am just using the motor for demonstration purpose I have used the +5V rail of the Arduino Board. Also remember to connect the Ground of the Arduino with the ground of the Driver module.
Code for Arduino Board:
Before we start programming with our Arduino, let us understand what should actually happen inside the program. As said earlier we will be using 4-step sequence method so we will have four steps to perform for making one complete rotation.
Step | Pin Energized | Coils Energized |
Step 1 | 8 and 9 | A and B |
Step 2 | 9 and 10 | B and C |
Step 3 | 10 and 11 | C and D |
Step 4 | 11 and 8 | D and A |
The Driver module will have four LED using which we can check which coil is being energised at any given time. The complete demonstration video can be found at the end of this tutorial.
In this tutorial we are going to program the Arduino in such a way that we can turn the potentiometer connected to pin A0 and control the direction of the Stepper motor. The complete program can be found at the end of the tutorial few important lines are explained below.
The number of steps per revolution for our stepper motor was calculated to be 32; hence we enter that as shown in the line below
Next you have to create instances in which we specify the pins to which we have connected the Stepper motor.
Note: The pins number are disordered as 8,10,9,11 on purpose. You have to follow the same pattern even if you change the pins to which your motor is connected.
Since we are using the Arduino stepper library, we can set the speed of the motor using the below line. The speed can range between 0 to 200 for 28-BYJ48 stepper motors.
Now, to make the motor move one step clockwise we can use the following line.
To make the motor move one step anti-clockwise we can use the following line.
In our program we will read the value of the Analog pin A0 and compare it with previous value (Pval). If it has increased we move 5 steps in clockwise and if it is decreased then we move 5 steps in anti-clockwise.
Working:
Once the connection is made the hardware should look something like this in the picture below.
Now, upload the below program in your Arduino UNO and open the serial monitor. As discussed earlier you have to rotate the potentiometer to control the rotation of the Stepper motor. Rotating it in clockwise will turn the stepper motor in clockwise direction and vice versa.
Hope you understood the project and enjoyed building it. The complete working of the project is shown in the video below. If you have any doubts post them on the comment section below or on our forums.
#include <Stepper.h> // Include the header file
// change this to the number of steps on your motor
#define STEPS 32
// create an instance of the stepper class using the steps and pins
Stepper stepper(STEPS, 8, 10, 9, 11);
int Pval = 0;
int potVal = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
stepper.setSpeed(200);
}
void loop() {
potVal = map(analogRead(A0),0,1024,0,500);
if (potVal>Pval)
stepper.step(5);
if (potVal<Pval)
stepper.step(-5); Nicholas carr does it matter pdf merger.
Pval = potVal;
Arduino Stepper Motor Serial Control Cable Box
Serial.println(Pval); //for debugging
}
Recommended Electronics Engineering Websites:
Hello friends! I hope you all will be absolutely fine and having fun. Today, I will elaborate you that how can we make a simple algorithm for Stepper Motor Direction Control using Arduino. In my previous tutorials I made algorithm for DC Motor Direction Control using Arduino, DC Motor Direction Control using Matlab, DC Motor Speed Control using Arduino and DC Motor Speed Control using Matlab. Now, in this tutorial I will control a stepper motor using Arduino by entering the different commands through its serial port.
Before going into the detail of this tutorial, you must know the basic difference between stepper and DC motors. DC motors have only two input terminal one is positive and the other one is negative. You just have to provide the power supply and it will start rotating but this is not the case in stepper motor. The stepper motor which I will use in this tutorial, has six pins out of which four pins provide pulses or steps and the other two pins are power pins. So, in this tutorial I will control this six pins stepper motor using L298 motor controller and Arduino UNO board. Basically we can use stepper motor where precision is required. Stepper motor has wide range of applications e.g robotics, CNC machines, home automation etc. In simple word, we can say that stepper motor can be used where there is a need to move at particular angle. So, let’s get started with Stepper Motor Direction Control using Arduino:
Stepper Motor Direction Control using Arduino
In this tutorial we will learn how to make a program for Stepper Motor Direction Control using Arduinoby sending dfferent commands from the serial port. First of all, I am going share the list of components used for this mini project.
- Arduino UNO
- Stepper motor (6 wire)
- L298 Motor Controller (H-Bridge)
- Voltage Regulator (7805)
- 1000uF
- Jumper Wires
- Solderig Iron
- Soldering Wire
I want to tell you a bit about the stepper motor because all the other components are discussed in detail in DC Motor Direction Control using Arduino.
Stepper Motor
Basically, stepper motors are like the DC motors that rotate in discrete steps. They have multiple arranged coils and they are usually known as phases. Motor will rotate one step at a time if we energize each phase sequence. High levels of precision can be achieved by controlling the stepper motor with computer. Steppers motors are available in the market in many different sizes. The speed of the stepper motor is controlled by frequency of pulses generated. They have wide range of applications like hard disk drives, robotics, telescope, antenna, toys etc. A six wire stepper motor is shown in the figure below.
- I have designed Stepper Motor Drive Circuit using Proteus ISIS and its screen shot is given in the figure below.
- You can download complete source code for Stepper Motor Direction Control using Arduino by clicking the below button:
Selection of Wires
- I have used 6 wire stepper motor and each wire has its own function.
- I have first divided these six wires into two pair.
- Each pair is consisting of three wires out of which one wire is common and the other two generate pulses.
- The two pair of three wires are shown in the figure below.
Stepper Motor Arduino Circuit
- After that. I checked the resistance between white and pink wire and found it to be 8.1 which is almost the same as 8.0 so, this shows that the white wire is common to both of the blue and pink wire.
- Here is the screen shot of the above step.
- Then I found the resistance between pink and blue wire and it was 15.6 which is exactly the double of the earlier resistance.
- It is shown in the figure below.
- I have connect the both common wires as shown in the figure below.
- Here’s the video in which I have discussed it in detail How to identify the wires of Stepper Motor:
Note:
I have also controlled the stepper motor using PIC micro controller so I would suggest all of you to first go through that tutorial before going into the details of this tutorial.Block Diagram
- I have made a simple block diagram for Stepper Motor Direction Control using Arduino, which will be helpful to clearly understand the algorithm and the assembling of the components of Stepper Motor Direction Control using Arduino.
- The screenshot of the block diagram is shown in the figure below.
- First of all we need a power supply to run the project properly.
- Arduino reads the commands from the serial port and sends to the L298 motor driver to rotate the stepper motor.
- The commands got printed on the LCD (Liquid Crystal Display).
Arduino Source Code Description
- The main function of the Stepper Motor Direction Control using Arduino is given below.
- In the code given above we have first initialized the LCD and Stepper motor libraries.
- Then, I assigned stepper motor pins at which it is connected to the Arduino.
- After that I initialized the LCD pins at which it is connected to Arduino UNO.
- Then I have made three different if statements, C for the clockwise, A for the anti clockwise rotation and S for the no rotation.
- Then in the loop I called clock wise and anti clockwise functions whose source code will be give and explained below.
- Then, I cleared the serial data in order to stop the rotation of the motor.
- The source code of the clockwise function is given below.
- The source code for the anti clockwise function is given below.
- Now, open your Arduino software, just copy and paste the source code given above.
- Run the program and open the Serial Port at the top right of the Arduino software.
- Now, when you enter the command C stepper motor will start running in clockwise direction.
- If you send the command A through the serial port stepper motor will start to rotate in counter clockwise direction.
- If you send the command S the rotation of the stepper motor will be stopped.
Actual Hardware Setup
- The actual hardware operating setup for Stepper Motor Direction Control using Arduino is given in the figure below:
- Now, if you send the command C through the serial port the stepper motor will start to rotate in clockwise direction and the command will also be printed on the LCD.
- The screenshot of the printed command on LCD is shown in the figure below.
- Now, if you send the command A through the serial port the stepper motor will start to rotate in anti clockwise direction and the command will also be printed on the LCD.
- The screenshot of the printed command on LCD is shown in the figure below.
- Now, if you send the command S through the serial port the stepper motor will show no more rotation and the command will also be printed on the LCD.
- The screenshot of the printed command on LCD is shown in the figure below.
- Here’s the complete video demonstration of Stepper Motor Direction Control using Arduino, I hope it will help as well:
That’s all from the tutorial Stepper Motor Direction Control using Arduino. I hope you enjoyed this tutorial. If you face any sort of problem, you can ask me anytime without feeling any kind of hesitation. I will try my level best to solve your problem in a better way if possible. I will explore Arduino by making different projects on it. Till then, Take care 🙂
JLCPCB – Prototype 10 PCBs for $2 (For Any Color)
China’s Largest PCB Prototype Enterprise, 600,000+ Customers & 10,000+ Online Orders Daily
How to Get PCB Cash Coupon from JLCPCB:
 Syed Zain Nasir3 Comments
Syed Zain Nasir3 Comments